WHERE TO START WITH DATA GOVERNANCE?
Hello! If you want to manage data properly, you need a structured plan. This is called a Data Governance Framework—think of it as a blueprint for handling data effectively.
Whether you’re a large company or a startup, if your data isn’t managed well, things can quickly become chaotic.
– Bad customer data? Your marketing fails.
– Weak security? A data breach could destroy your company.
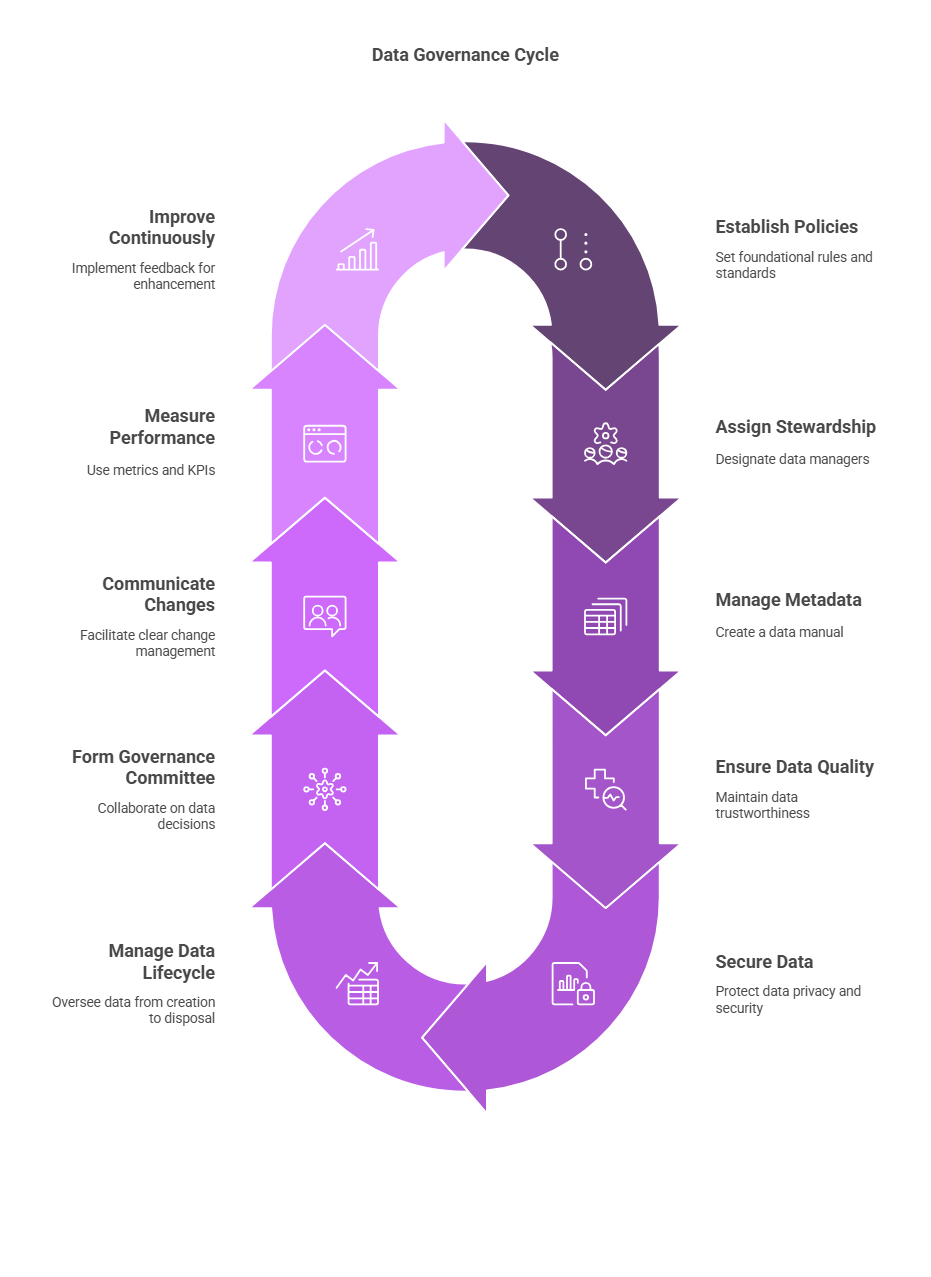
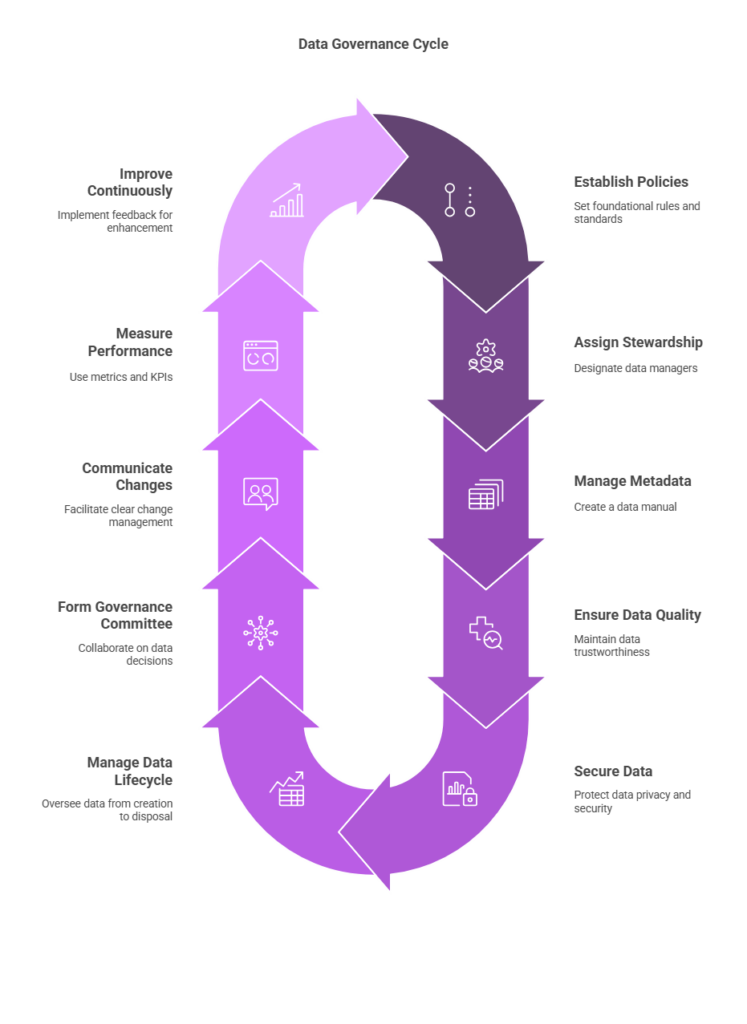
That’s why building a solid governance framework is essential! Today, we’ll break it down into 10 key components so you can understand it easily.
Ready? Let’s dive in!
1. Data Policies & Standards: Set the Rules First!
o What is it?
- Policies are broad guidelines, while standards are specific rules.
- Example: A policy might say, “Customer data must be anonymized before sharing.”
- A standard defines how: “Use AES-256 encryption for anonymization.”
o Why is it important?
- Prevents confusion—without rules, every team manages data differently.
- Ensures consistency—everyone follows the same standards.
o Example:
A startup decided that before sharing customer data externally, they must first anonymize it. They also set an encryption standard—this keeps their data secure!
2. Data Stewardship: Who’s in Charge?
o What is it?
- Data Stewards manage and maintain data quality.
- They enforce policies and fix data issues.
o Why is it important?
- Without a Steward, each team manages data their own way—leading to data silos.
- Stewards bridge the gap between teams and ensure collaboration.
o Example:
A marketing team has a Data Steward who ensures their customer segmentation data is accurate. Without proper segmentation, marketing wastes money on bad ads!
3. Metadata Management: Creating a Data Dictionary
o What is it?
- Metadata is information about data—where it came from, how it’s structured, and how it should be used.
- Think of it as a data catalog that helps teams understand what data means.
o Why is it important?
- Without metadata, data is hard to find and even harder to use correctly.
o Example:
A company uses a metadata repository to track customer data origins.
– Now, analysts can see: “This data came from our CRM and was last updated in Q4.”
4. Data Quality Management: Is Your Data Reliable?
o What is it?
- Ensures data is accurate, complete, and consistent.
- Fixes issues like missing or duplicate data.
o Why is it important?
- Bad data = bad decisions. If customer data is wrong, ads are wasted and customer service suffers.
o Example:
A company automates data profiling—detecting missing addresses and duplicate names before they cause problems.
5. Data Security & Privacy: Keep Data Safe!
o What is it?
- Security protects against hacks and breaches.
- Privacy ensures compliance with regulations (like GDPR).
o Why is it important?
- Companies lose millions from data breaches and privacy violations.
o Example:
A finance company uses Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to ensure only authorized employees can view sensitive data.
6. Data Lifecycle Management: Managing Data from Birth to Deletion
o What is it?
- Controls how data is created, stored, used, archived, and deleted.
- Prevents overcrowding systems with old, unnecessary data.
o Why is it important?
- Saves storage costs and reduces risk of outdated data being used.
o Example:
A startup keeps customer transaction data for 7 years, then automatically archives it.
7. Data Governance Committee: Making Strategic Decisions
o What is it?
- A group of business leaders, IT teams, and compliance experts.
- Sets data governance policies and resolves conflicts.
o Why is it important?
- Ensures data governance aligns with business strategy.
- Prevents one team from dominating data decisions.
o Example:
A governance committee reviews data-sharing policies before approving partnerships with third parties.
8. Change Management & Communication: Keep Everyone Aligned
o What is it?
- Manages policy changes and communicates updates across teams.
o Why is it important?
- A policy that nobody knows about is useless.
o Example:
When a company introduced a new data classification system, they provided training sessions so employees understood how to categorize and protect data.
9. Metrics & KPIs: Measuring Success
o What is it?
- Tracks how well data governance is working.
- Examples: Data quality scores, compliance rates, issue resolution times.
o Why is it important?
- Without metrics, you can’t tell if your governance is effective or failing.
o Example:
A company set a goal: “Data quality must be above 95%”—and used KPIs to measure and improve it.
10. Continuous Improvement: Keep Evolving!
o What is it?
- Regularly review, audit, and update governance policies.
- Adjust to new threats, technologies, and regulations.
o Why is it important?
- Data governance isn’t a one-time project—it needs constant updates.
o Example:
After a data breach, a company reviewed its incident response plan and made improvements to prevent it from happening again.
11 Data Governance is Like Growing a Tree 🌱
These 10 components make up a strong data governance framework:
– Policies set the rules.
– Stewards manage data quality.
– Security protects sensitive data.
– Lifecycle management prevents data overload.
– Continuous improvement keeps governance effective.
Think of data governance like growing a tree—it requires ongoing care to keep it strong and healthy.
Previously, I introduced the five core principles of data governance. Now, let’s break them down into ten actionable pillars for a more structured and practical implementation.
| Core Principle | Mapped Pillars (Rules) | Description |
| Policies & Rules | 1. Data Policies & Standards 6. Data Lifecycle Management | Establishes foundational rules and lifecycle policies for managing data throughout its lifespan. |
| Data Quality | 3. Metadata Management 4. Data Quality Management 9. Metrics & KPIs | Ensures data is understood, maintained, and measured for accuracy and reliability. |
| Security & Privacy | 5. Data Security & Privacy | Ensures data protection, compliance, and privacy regulations are upheld. |
| Roles & Responsibilities | 2. Data Stewardship 7. Data Governance Committee 8. Change Management & Communication | Clearly defines who is responsible for what, ensures collaboration, and manages policy updates & communication. |
| Technology & Tools | 10. Continuous Improvement & Feedback Loop 6. Data Lifecycle Management | Leverages technology to support automation, efficiency, and governance enhancements. |